January 2026 Vol. 81 No. 1
Features
2026 outlook bright for utility and communications construction markets
By Daniel Shumate, Managing Director, FMI Capital Advisors Inc.
(UI) — 2025 represented a largely incredible year for utility and communications construction, with several converging trends positively shaping the sector. With the exception of some capital expenditures tied to renewable generation, demand drivers such as resiliency, data centers, interconnection and population growth supported strong backlog and profitability for companies serving the underground construction market.
Looking ahead to 2026, optimism remains high. Two dominant forces — data centers and rising power demand — are expected to have the greatest impact on contractors across the industry.
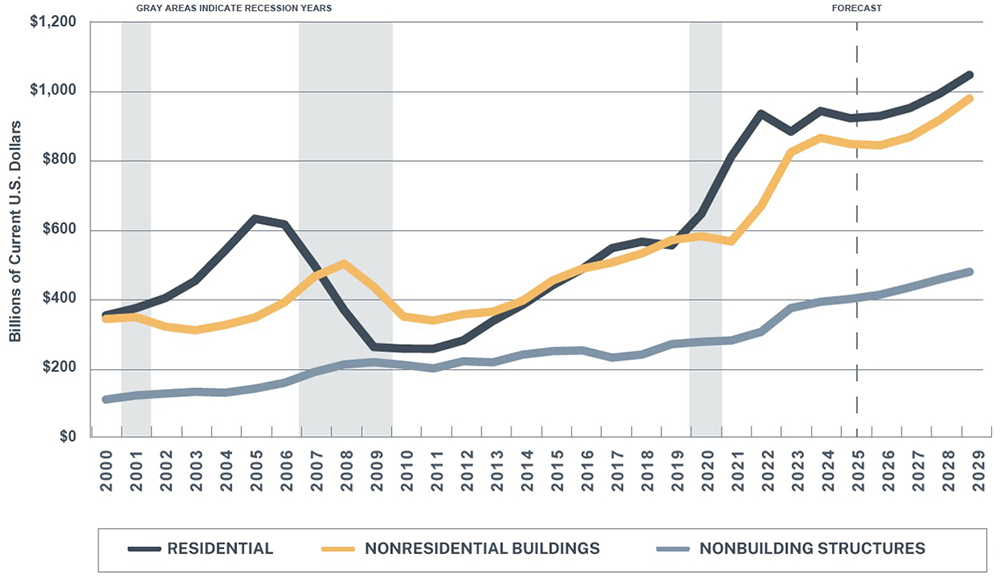
The U.S. utility construction market includes new construction captured in FMI’s Construction Outlook, as shown in Figure 1. The steady growth in non-building structures construction is expected to continue above inflation in the coming years. In addition, a significant portion of utility work across power, gas, water and wastewater pipelines consists of repair and replacement activity not reflected in new construction data. Together, these factors point to a strong and expanding market entering 2026.
Theme 1: Power, data centers, and the supporting infrastructure driving the next wave of growth
One of the most powerful demand drivers entering 2026 is the continued expansion of data centers and power infrastructure. In some markets, data centers account for more than 25% of total nonresidential building construction. While this trend was already emerging last year, it remains a central force shaping construction spending and resource allocation.
The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence is accelerating data center development and dramatically increasing demand for reliable, resilient and scalable power. Power availability has become the primary constraint on site selection and development timelines. Berkeley Lab estimates that data centers could consume between 325 and 580 TWh annually by 2030 — representing 7% to 12% of total U.S. electricity use — placing additional strain on transmission, distribution and generation infrastructure.
Data center growth depends on power availability, grid interconnection and fiber access. Contractors and engineers with proven experience in transmission interconnections, substations and wet and dry utilities — particularly those with strong track records in safety, scheduling and risk management — are well positioned to capture multi-year backlog from these increasingly complex projects.
Foundational requirements
Sustainability and electrification are no longer driven solely by policy mandates or corporate commitments. They are becoming core economic and operational considerations as rising energy demand, increasing electricity costs and extreme weather exposure push owners and public agencies toward resilient and durable infrastructure.
State and local governments are tightening climate resilience requirements while federal funding priorities continue to shift. Investments in distributed energy resources and resilient design are increasingly shaped by reliability, risk mitigation and speed to market.
Climate-related disasters continue to rise in frequency and cost. In 1980, the U.S. experienced three billion-dollar climate disasters; by 2024, that number had grown to 27, resulting in more than $182.7 billion in damages. These trends are accelerating investment across the utility infrastructure value chain.
Power transmission and distribution
Investment in power transmission and distribution expanded significantly in 2025 and is expected to continue through 2026. According to EEI, investor-owned utilities spent nearly $40 billion on transmission investment in 2025 and expect to grow spending by 7% to 8% annually. Between 2025 and 2028, utilities plan to invest approximately $178 billion in transmission construction — the largest investment cycle the U.S. has experienced.
Power distribution spending is expected to follow a similar trajectory, supported by interconnection work, resiliency upgrades, overhead-to-underground programs and continued repair of legacy infrastructure. Growth of 8% to 10% in the distribution segment is feasible under current market conditions.
Natural gas transmission and distribution
The outlook for natural gas transmission differs under the Trump administration. Some of the strongest years for pipeline construction occurred during President Trump’s first term, and project backlogs entering 2026 remain meaningful. Growth is concentrated in the Marcellus and Permian basins and is expected to continue.
For gas distribution contractors, installation, repair and replacement will remain priorities. While early-stage replacement programs have largely been completed, utilities are increasingly focused on dense urban environments and congested corridors, where costs are higher and execution more complex. Cost pressures remain a key concern for utility commissions, contributing to phased or delayed program rollouts.
Communications infrastructure
The communications construction sector expects the BEAD program to transition from planning to construction in 2026. While administrative delays tied to the IIJA have frustrated contractors, engineering reviews are expected to give way to active construction.
2026 could be one of the strongest years on record for FTTH and competitive metro builds. Capital expenditures from major telecommunications providers remain robust and nationwide in scale, supporting optimism across the sector.
Municipal water and wastewater
Water and wastewater markets are expected to grow meaningfully in 2026, with FMI projecting growth exceeding 7%. Drivers include water treatment plant construction, lead service line replacement, underground pipeline repair, source water protection and increased demand from industrial and data center cooling.
Meter modernization and leak detection programs are also expanding as utilities invest in advanced metering infrastructure to reduce non-revenue water. However, uncertainty remains around federal funding. The proposed FY 2026 budget includes an 89% reduction in CWSRF funding, which could push states toward alternative financing options such as municipal bonds and public-private partnerships.
UCCI performance, updates
The Utility & Communications Construction Index (UCCI) presented below presents the stock performance of the sector’s publicly traded stocks over the past year (Figure 2) and the past three years (Figure 3).
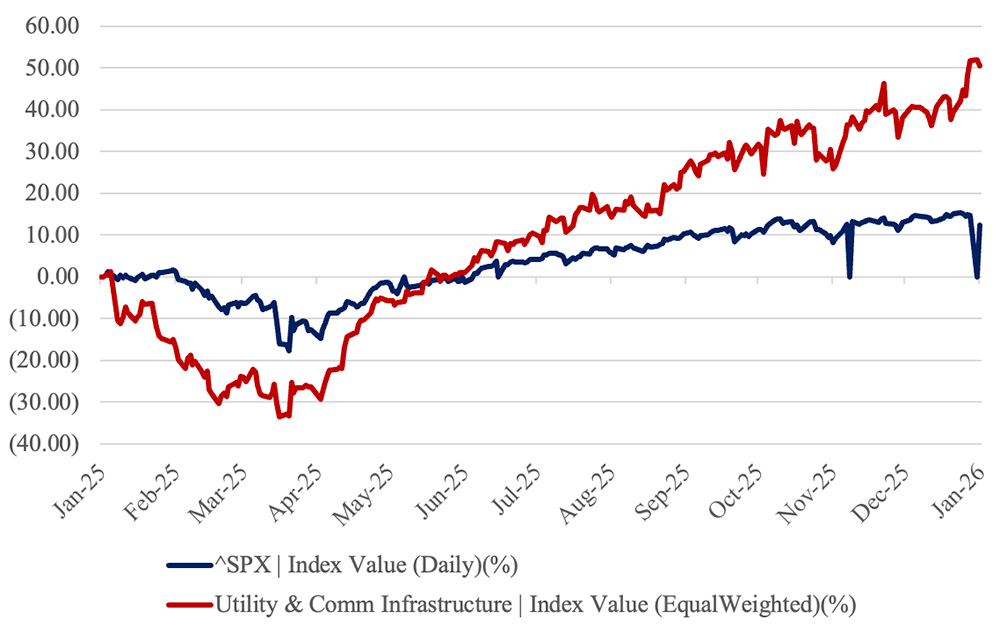
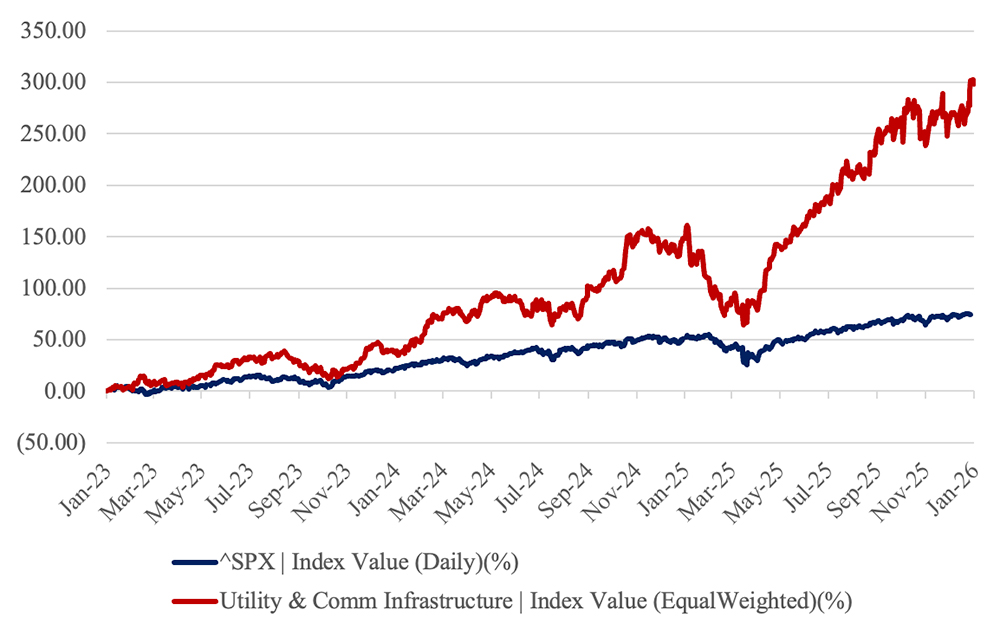
The last 12-month performance of the UCCI is up over 50 percent on the year because of the expectation for sustained growth and spending on utility and communications infrastructure. Additionally, this occurs while the stock market surpassed its all-time highs throughout the year.
The UCC Index outpaced the S&P 500, which increased by 12.5 percent over the past 12 months. Market expectations for revenue and earnings growth will continue to rise and while there are numerous strong fundamental elements of the utility infrastructure market, continued growth at these rates will be challenging.
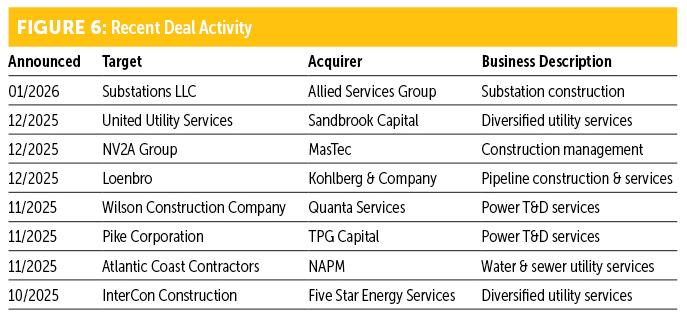
Mergers and acquisitions
The final quarter of activity in 2026 saw multiple completed transactions that continue to reshape the utility and communication construction markets. Despite global uncertainty, long-term macro trends continue to support mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity across the utility infrastructure segment.




Comments